Droonga 1.0.8 has been released!
2014-11-29What’s Droonga?
Droonga is a distributed full text search engine, compatible to Groonga. A Droonga cluster works like an HTTP server compatible to Groonga with the replication feature.
Are you interested in Droonga: how it works and how useful? Let’s try the tutorial for an introduction, and see the overview to understand Droonga’s design strategy more and more.
Improvements in Droonga 1.0.8
This release Droonga 1.0.8 contains many improvements. Major topics are here:
Orchestration of front-end HTTP server nodes
A front-end HTTP server node based on droonga-http-server has become to a member of the Droonga cluster truly.
In old versions, a droonga-http-server node was strongly bound to a droonga-engine node.
So, if a droonga-engine node died, droonga-http-server nodes associated to the droonga-engine node also died.
But now, the limitation has been gone.
Even if one of droonga-engine node become unavailable, droonga-http-server nodes keep them working with active droonga-engine nodes automatically.
Moreover, a droonga-http-server node distributes requests from clients to multiple droonga-engine nodes.
In other words, now it works like a simple load balancer.
Better performance for search operations, especially with groupBy (Groonga’s select with drilldown options)
The performance issue around groupBy is solved for replicas with single slices.
Moreover, search operations with offset option also optimized.
Benchmark results (comparisons with Groonga) are here:
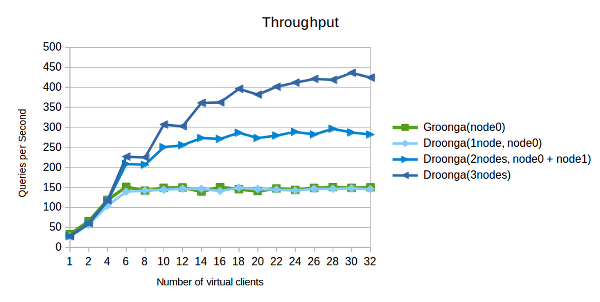
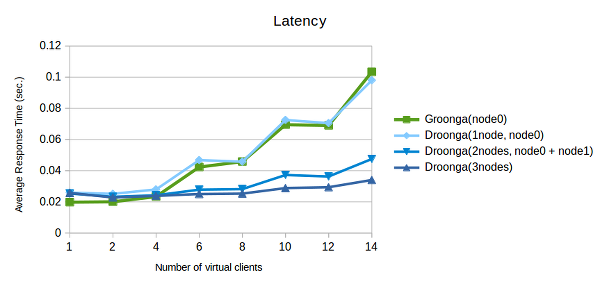
Conditions:
- There are 1500000 records from Wikipedia (Japanese)
- All requests are full-text search queries for actual page titles, with drilldown, like:
/d/select?command_version=2&table=Pages&limit=10&match_columns=title,text&output_columns=snippet_html(title),snippet_html(text),categories,_key&query_flags=NONE&sortby=title&drilldown=categories&drilldown_limit=10&drilldown_output_columns=_id,_key,_nsubrecs&drilldown_sortby=_nsubrecs&query=Wikipedia%3AText+of+GNU+Free+Documentation+License - Supposed cache hit rate is 50%.
- Measured on physical PCs for development.
- node0: Ubuntu 14.04LTS, Intel Core i5 M460 2.53GHz, 8GB RAM
- node1: Ubuntu 14.04LTS, Intel Core i5 650 3.20GHz, 6GB RAM
- node2: Ubuntu 14.04LTS, Intel Core i5 650 3.20GHz, 8GB RAM
- client: Ubuntu 14.04LTS, Intel Core i5-4300U vPro 1.90GHz, 4GB RAM
Detailed results are downloadable.
As above, currently throughput performance of single Droonga node is comparable to Groonga. Moreover, throughput limit can be extended by adding more Droonga nodes to the cluster.
On the other hand, there is a little latency basically on Droonga. However, large number accesses turn the advantage around the upper limit of Groonga. If there are too many requests, Droonga can respond quickly than Groonga.
Better compatibility to Groonga
Some minor incompatibilities have been corrected.
selectcommand:- The
output_columnsoption accepts whitespace-separated list of column names (compatible to Groonga’scommand_version=1form.) output_columns=*works correctly forTABLE_NO_KEYtables.
- The
column_listcommand:- A
_keyvirtual column is correctly appear in the result, for tables with one of flags:TABLE_HASH_KEY,TABLE_PAT_KEY, andTABLE_DAT_KEY. - At an index column, its
sourceis now compatible to Groonga’s one.
- A
table_createcommand:- The
key_typeparameter becomes required forTABLE_HASH_KEY,TABLE_PAT_KEY, andTABLE_DAT_KEYtables. You’ll get an error response, if the parameter is not given. (Groonga unexpectedly acceptstable_createrequests withoutkey_typeparameter, but it is a known issue.)
- The
Detailed list of all improvements
- Droonga-engine 1.0.8
- Better compatibility to Groonga’s
select,column_list, andtable_createcommands. (See above) - The
daemonoption is now ignored in the static configuration file. Now, you always have to specify--daemonoption for thedroonga-enginecommand to start it as a daemon. - The
droonga-engine-configurecommand now shows prompts for all options always. - The rate of absorbed records are limited to 100 records per second by default, for
droonga-engine-absorb-dataanddroonga-engine-joincommands. droonga-engine-absorb-dataanddroonga-engine-joincommands now report their progress, if possible.
- Better compatibility to Groonga’s
- Droonga-http-server 1.0.9
- A new
--hostoption is available to restrict the listening IP address. The default value is0.0.0.0(meaninglisten all IP addresses). - A new
--cache-ttl-in-secondsoption is available to set the time to live of cached responses, in seconds. The default value is60(meaning1 minute). - A new
--disable-trust-proxyoption is available to disable the feature even if it is activated by the static configuration file. - A new
--document-rootoption is available to specify the document root. It is the path to the built-in Groonga admin page by default. - The
daemonoption is now ignored in the static configuration file. Now, you always have to specify--daemonoption for thedroonga-http-servercommand to start it as a daemon. - The
droonga-http-server-configurecommand now shows prompts for all options always. - Responses for most commands are never cached.
Now, only responses based on
searchor Groonga’sselectcommands and the administration page are cached. - A new endopoint
/cacheis introduced to clear all response caches. To clear cached contents, send an HTTPDELETErequest to the path. - Improvements from
express-droongaitself. (See below)
- A new
- Express-droonga 1.0.7
- Supports multiple Droonga Engine nodes as its backends.
Now
express-droongacan work like a load balancer. - The list of connecting Droonga Engine nodes can be automatically updated
based on the actual list of active members in the cluster.
This feature is activated by the
syncHostNamesoption for theapplication.droonga()method.
- Supports multiple Droonga Engine nodes as its backends.
Now
- Drnbench 1.0.4
drnbench-request-response- Not only top slow requests, but top fast requests are also reported.
It will help you to detect “strange good” results from invalid queries or something.
The number of reported fast requests can be customized via the new
--n-fast-requestsoption. - Virtual clients are working with multiple processes. If there are multiple processors in your computer, drnbench uses them more effectively.
- Not only top slow requests, but top fast requests are also reported.
It will help you to detect “strange good” results from invalid queries or something.
The number of reported fast requests can be customized via the new
- Drntest 1.1.7 (released at 2014-11-18)
- Accept virtual column like
_keyas a part of Groonga’scolumn_listcommand response.
- Accept virtual column like
Conclusion
- Droonga 1.0.8 has been released!
- Front-end HTTP server nodes are now orchestrated as nodes in the cluster. Droonga clusters now work more robustly.
- The throughput performance is comparable to / better than Groonga now.
- It becomes more compatible to Groonga.
- Droonga project will release a new version every month!
Droonga project welcomes you to join us as a user and/or a developer! See community to contact us!